
In our Frequently Asked Questions about calprotectin series we will answer questions we often receive about plasma and serum calprotectin and the Gentian Calprotectin Immunoassay GCAL®. If you have any additional questions don't hesitate to contact us on marketing@gentian.com.
In this section we will look into why plasma and serum calprotectin is upregulated in COVID-19?
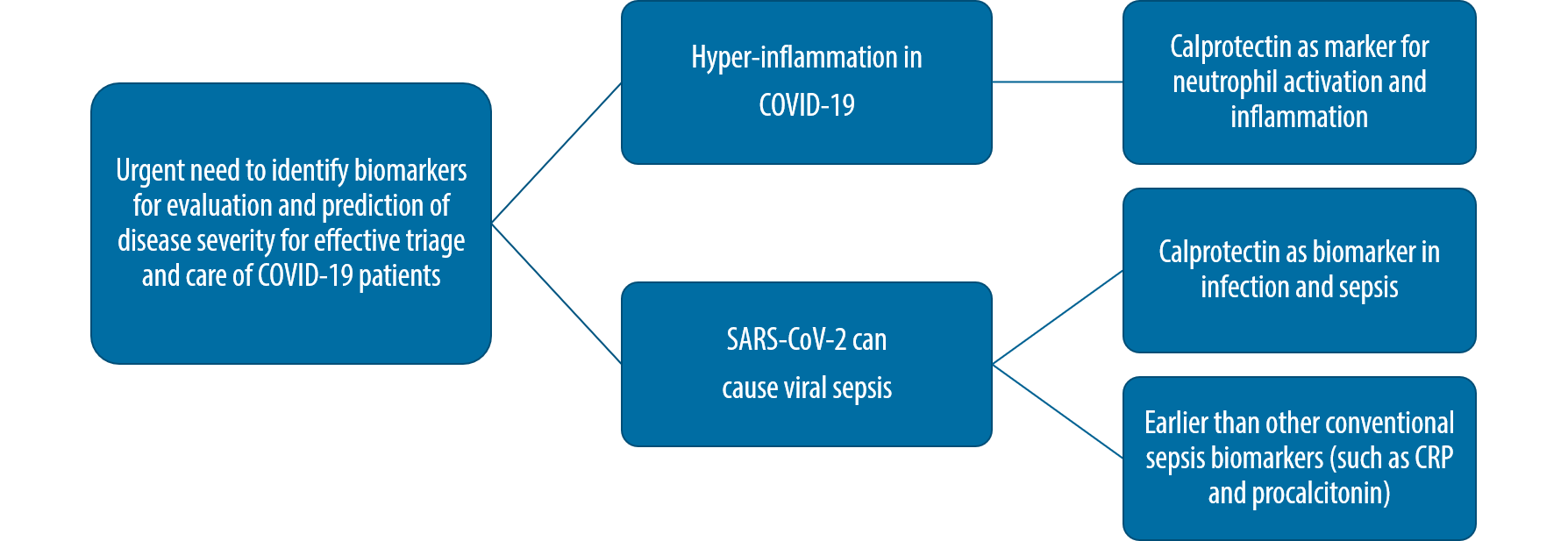
Viral sepsis in COVID-19
Plasma and serum calprotectin has been described as specific biomarker for the inflammatory response in severe bacterial infections and sepsis, where it is able to distinguish between viral and bacterial infections1-3. But why is it upregulated in the viral infection COVID-19 and what is the link to sepsis?
SARS-CoV-2 has been described to cause viral sepsis in several studies4-9. This is also reported by the Global Sepsis Alliance. Patients with severe COVID-19 have shown symptoms of sepsis and septic shock, including including fever and chills, fatigue or weakness, cold extremities and weak peripheral pulses. Hospitalised COVID-19 patients with severe form of the disease have also alterations in the coagulation, dysregulated immune response and induction of cytokine response also called cytokine storm, the response which is very similar to bacterial sepsis6,10-13. In fact, many severe COVID-19 patients meet the criteria of the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis (Sepsis‐3). Most of COVID-19 deaths are caused by sepsis7,10,14.
Calprotectin is upregulated and activated in COVID-19 patients
SARS-CoV-2 infections differ from other viral infections because severe COVID-19 patients display symptoms of immune dysregulation and hyperinflammation15. The cytokine storm is described in many severe COVID-19 patients. It is characterised by a high production of cytokines resulting in increased inflammation7,8,11,16.
Neutrophils are upregulated and activated in COVID-19 patients as potential driver of disease severity15,17,18. Calprotectin is marker for neutrophil activation19,20 and has also been shown to correlate with increased cytokines in COVID-1921.
In the light of the similarities of bacterial and viral sepsis, it is sensible that calprotectin, as biomarker in bacterial sepsis22-24, is elevated in severe COVID-19. Indeed, calprotectin has been reported to be elevated in COVID-19 patients correlating with disease severity, and plasma and serum calprotectin has been described as promising biomarker for risk stratification21, 25-29.
COVID-19, sepsis and calprotectin:
- SARS-CoV-2 can cause viral sepsis in severe COVID-19 and viral sepsis is the leading cause of COVID-19 mortality
- Patients with severe form of COVID-19 display immune dysregulation, cytokine storm and hyperinflammatory host response
- The use of calprotectin in risk assessment in severe COVID-19 is comparable to its use in bacterial sepsis
GCAL® – Gentian’s Calprotectin Immunoassay
- Particle-Enhanced Turbidimetric Immunoassay (PETIA)
- Serum and plasma samples
- Rapidly performed in only 10 minutes
- Can be applied on a wide range of automated clinical chemistry analysers
- Avian antibodies – less interference
- CE-marked
Get in touch
For more details about the Gentian Calprotectin Immunoassay GCAL® please contact us at marketing@gentian.com or fill out the form below:
FAQ about plasma and serum calprotectin
What type of assay is the Gentian Calprotectin Immunoassay GCAL®?
What is calprotectin’s role in neutrophil activation?
What is the value of calprotectin in blood as biomarker in IBD?
What is the clinical value of calprotectin in severe infections?hat is the clinical value of calprotectin in sepsis & severe infections?
What role can plasma & serum calprotectin play in severe COVID-19?
How is calprotectin useful to monitor treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis?
How is calprotectin useful in clinical assessment of rheumatoid arthritis?
What role has circulating calprotectin in vasculitis?
References
- Havelka A et al. Calprotectin, a new biomarker for diagnosis of acute respiratory infections. Scientific reports. 2020.
- Siljan WW et al. Inflammatory biomarkers are associated with aetiology and predict outcomes in community-acquired pneumonia: results of a 5-year follow-up cohort study. ERJ Open Res. 2019.
- Bartáková E et al. Calprotectin and calgranulin C serum levels in bacterial sepsis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019.
- Vincent JL. COVID-19: it's all about sepsis. Future Microbiol. 2021.
- Shappell CN et al. Does Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Cause Sepsis? Crit Care Med. 2020.
- Li H et al. SARS-CoV-2 and viral sepsis: observations and hypotheses. Lancet. 2020.
- López-Collazo E et al. Immune Response and COVID-19: A mirror image of Sepsis. Int J Biol Sci. 2020.
- Odabasi Z, Cinel I. Consideration of Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 As Viral Sepsis and Potential Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Crit Care Explor. 2020.
- Liu D et al. Viral sepsis is a complication in patients with Novel Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19). Med Drug Discov. 2020.
- Beltrán-García J et al. Sepsis and Coronavirus Disease 2019: Common Features and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Approaches. Crit Care Med. 2020.
- Colantuoni A et al. COVID-19 Sepsis and Microcirculation Dysfunction. Front Physiol. 2020.
- Sohn KM et al. COVID-19 Patients Upregulate Toll-like Receptor 4-mediated Inflammatory Signaling That Mimics Bacterial Sepsis. J Korean Med Sci. 2020.
- Wilson JG et al. Cytokine profile in plasma of severe COVID-19 does not differ from ARDS and sepsis. JCI Insight. 2020.
- Hantoushzadeh S, Norooznezhad AH. Possible Cause of Inflammatory Storm and Septic Shock in Patients Diagnosed with (COVID-19). Arch Med Res. 2020.
- Guo Q et al. Induction of alarmin S100A8/A9 mediates activation of aberrant neutrophils in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe. 2020.
- Olwal CO et al. Parallels in Sepsis and COVID-19 Conditions: Implications for Managing Severe COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2021.
- Zuo Y et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. JCI Insight. 2020.
- Barnes BJ et al. Targeting potential drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil extracellular traps. J Exp Med. 2020.
- Wang S et al. S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2018.
- Pruenster M et al. S100A8/A9: From basic science to clinical application. Pharmacol Ther. 2016.
- Chen L et al. Elevated serum levels of S100A8/A9 and HMGB1 at hospital admission are correlated with inferior clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020.
- Wirtz TH et al. Association of Serum Calprotectin Concentrations with Mortality in Critically Ill and Septic Patients. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020.
- Jonsson N et al. Calprotectin as an early biomarker of bacterial infections in critically ill patients: an exploratory cohort assessment. Crit Care Resusc. 2017.
- Larsson A et al. Calprotectin is superior to procalcitonin as a sepsis marker and predictor of 30-day mortality in intensive care patients. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. 2019.
- Luis García de Guadiana R et al. Circulating levels of GDF-15 and calprotectin for prediction of in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: A case series. J Infect. 2020.
- Bauer W et al. Outcome prediction by serum calprotectin in patients with COVID-19 in the emergency department. J Infect. 2020.
- Silvin A et al. Elevated Calprotectin and Abnormal Myeloid Cell Subsets Discriminate Severe from Mild COVID-19. Cell. 2020.
- Shi H et al. Neutrophil calprotectin identifies severe pulmonary disease in COVID-19. Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 2020.
- Udeh R et al. Calprotectin, an Emerging Biomarker of Interest in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021.


-1.jpg)
.png)